SaaS Business Model Simplified: Your Roadmap to App Success

SaaS (Software as a Service) was originally coined in the 1990s. Although it has been long decades in the technology industry, the SaaS business model is still in its infancy in business in general.
Whether you’re looking to boost revenue and app ROI or just starting to develop an app idea, you’re in the right place to know more about this model.
According to Gartner, the SaaS industry is forecast to grow 20.7% to a total of $591.8 billion in 2023.
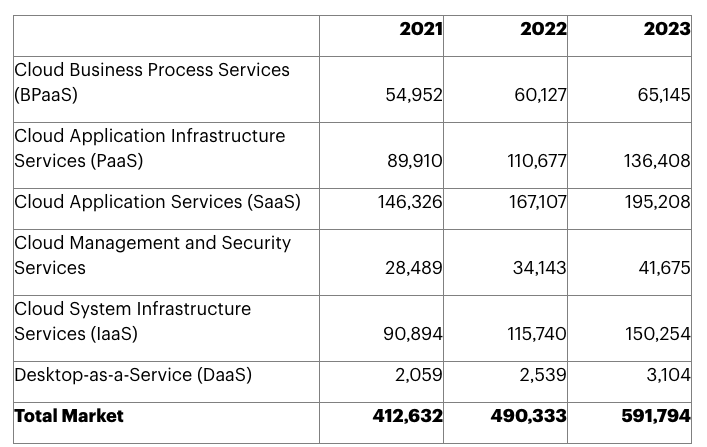
Source: Gartner
So, how do you embrace the SaaS business models without getting overwhelmed with the jargon?
This guide will serve as your roadmap as I simplify the components of the SaaS business model. By the end of this article, you’ll learn how each part directly impacts your next steps toward mobile app profitability.
What is a SaaS business model?
A SaaS (Software as a Service) business model is a business strategy that involves providing software applications and services to customers through a cloud-based distribution system. In this model, the software is hosted on remote servers and is accessed through the Internet. It allows customers to use the software without needing on-premises hardware or software installations.
However, SaaS businesses can go beyond the intricacies of IT infrastructure and RevOps. You also need to know how to run the company at each stage. According to Younium, SaaS business models use cloud delivery technology to provide their services such automatic billing, revenue recognition, entertainments content with their customers.
3 stages of a SaaS business model explained
Every business needs to transition for growth. If they are deep-pocketed brands, some will even go the extra mile by working with a SaaS SEO agency.
Here are the three stages you could expect to go through:
🚀 Early stage or pre-startup stage
This stage entails the period before the company’s launch. It’s when entrepreneurs identify a gap in the market they can address with a SaaS solution. 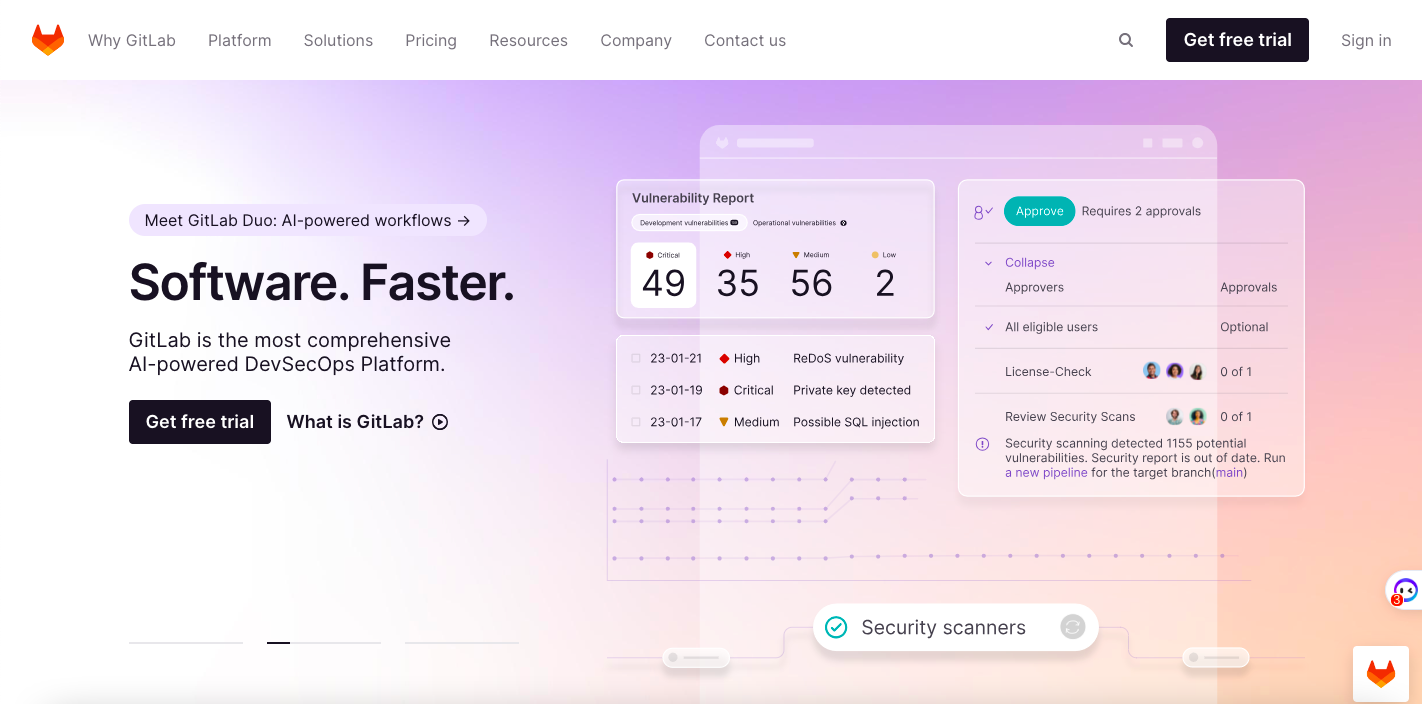
Source: GitLab
A perfect example of a SaaS company in this stage is GitLab, a Git repository and collaborative platform for developers. The founders looked for a project management tool that didn’t exist, so they created it themselves.
They started as a one-man company in 2011 and launched the first version of GitLab, followed by a continuous integration tool in 2012.
🚀 Startup or growth stage
The Startup/Growth stage is characterized by the period when the company is gaining traction and the product is being developed and refined. For starters, building a minimum viable product (MVP) app is also ideal to see how your target audience responds initially to basic features.
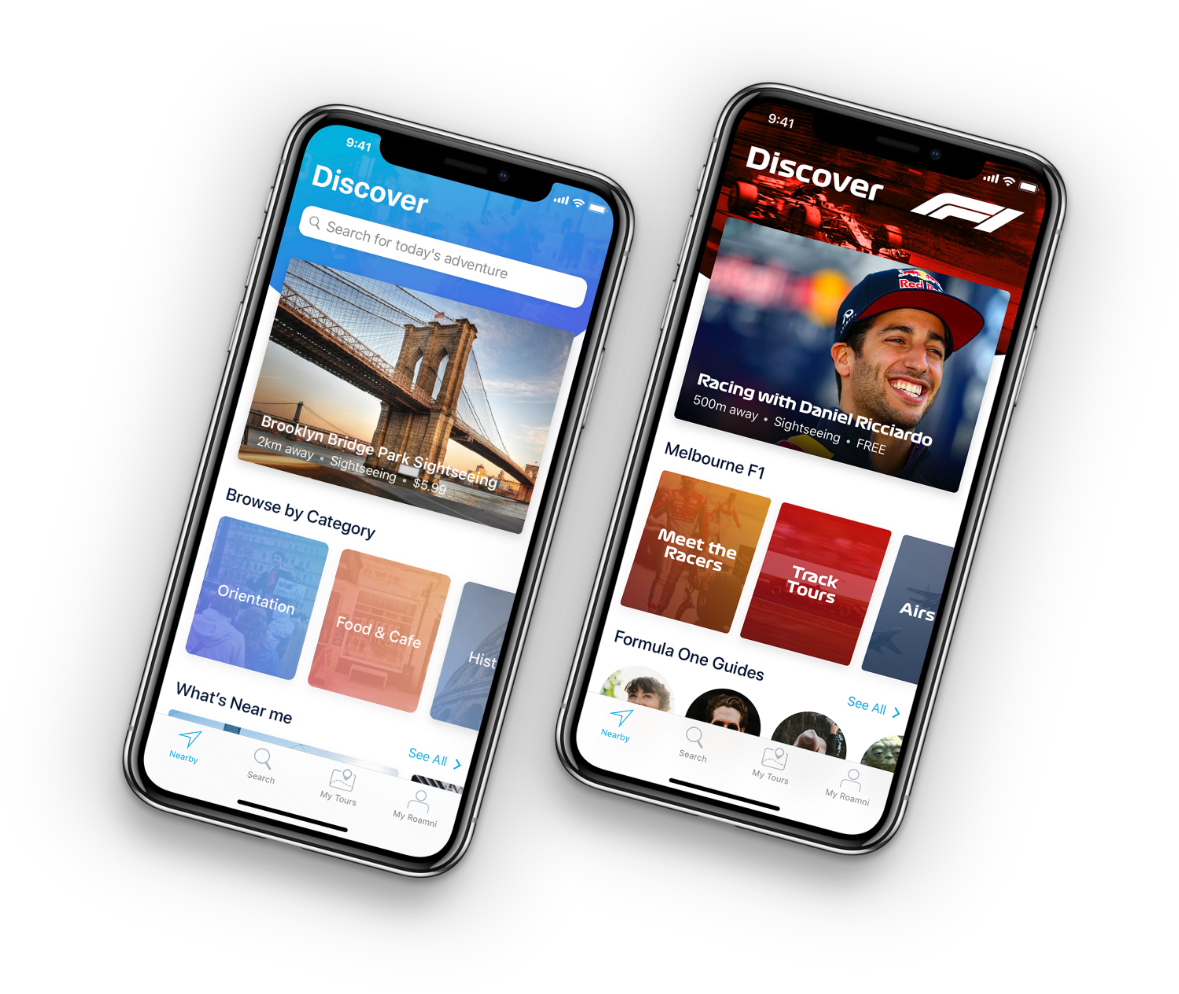
A prime example of a company in this stage is Roamni.
Roamni was born from a genuine problem – how to share, create, and experience local stories. The founders partnered with Appetiser, leveraging our mobile app development expertise.
💡 In just six weeks, Roamni’s strategy and design produced a powerful prototype. Their unique app design highlighted its features, tested the waters, reduced risk, and attracted investor interest. Within three years, Roamni became Formula 1’s official partner, now valued at over $5 million as a successful startup.
🚀 Maturity or expansion stage
A SaaS business’s maturity or expansion stage is when the product has proven successful, and the company is expanding and scaling up.
When planning a SaaS startup, it’s crucial to consider how you will effectively manage your company’s financial future. Utilizing comprehensive budgeting and projections tools can streamline this process, offering a coherent framework for scenario planning on the fly, fostering swift responses to market changes, and enabling collaborative forecasting among team members.
MyDeal is one of the successful startups that has reached this milestone.
Recognizing the power of action and forward momentum in app development, the founder confidently bootstrapped the platform in its early years without waiting for investors.
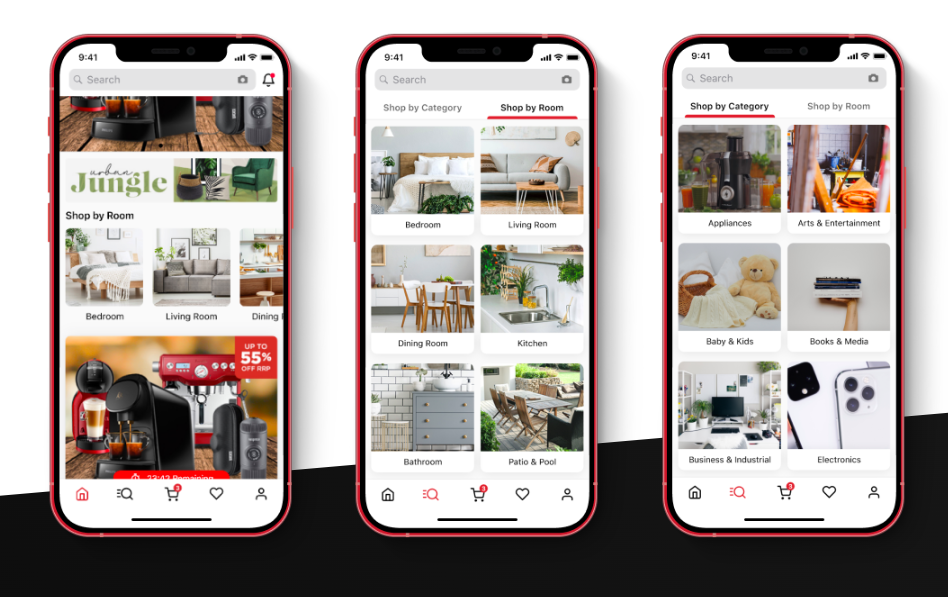
In 2020, he approached us to help realize his vision of an app that would reach new audiences and enhance the mobile shopping experience for over 883,000 active customers.
Together, we collaborated and built an app, which led MyDeal to surpass recognized brands like H&M and IKEA in app store dominance. That year, the startup went public on the Australian Stock Exchange, with our app playing a pivotal role.
📣 In 2021, gross sales increased by 111.1%. Now, supermarket giant Woolworths has already acquired 80% of the online marketplace, valuing the 10-year-old company at an impressive AUD 243 million.
What makes SaaS business model different from other business models
Now, to give you a broader perspective of SaaS, I’ve compiled a comparison table below for each section and short explanations for what makes it different from other business models.
But first, here are some notable features of a SaaS business model:
- ✅ The business sells a software service via the cloud.
- ✅ The pricing model is usually subscription-based.
- ✅ The priority is more on customer service and retention.
- ✅ The SaaS revenue model is ongoing and somewhat predictable since you earn from subscriptions (monthly, quarterly, bi-annually, or annually).
- ✅ The service can scale and serve a large number of users quickly.
| SaaS | eCommerce | Content | Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software service via cloud computing | Online marketplaces | Blogs, videos, podcasts, and other digital forms | Per project basis |
| Uses subscription-based | Uses a transactional revenue model | Uses affiliate marketing, sponsorship | Uses one-time fee payment or retainer’s fee for long-term projects. |
| Prioritizes customer service and retention | Prioritizes customer acquisition over retention | Prioritizes both customer acquisition and retention | Prioritizes both customer acquisition and retention |
| Predictable sales and revenue | Unpredictable sales and revenue | Unpredictable sales and revenue | Unpredictable sales and revenue |
| Scalable and flexible | Non-scalable and limited | Scalability depends on the number of paying customers | Non-scalable and limited unless there are more service providers |
eCommerce business model
- The business sells products through online marketplaces, such as Amazon or eBay.
- The payment is a transactional model, where companies earn revenue from individual product sales.
- The priority is more on acquiring new customers over retention to get more sales. This often leads Amazon marketplace sellers to work with an Amazon marketing agency as part of their acquisition strategy, though results can vary
- The revenue can be unpredictable as everything depends on stocks and inventory management.
- The shop can’t serve a large number of customers if there are only limited number of items on hand.
Content-based business model
- The business creates and distributes content like articles, videos, or podcasts.
- Monetization can be done in various ways, such as through advertising, sponsorships, or affiliate marketing.
- The content-based businesses can have a wide appeal and make excellent acquisitions for first-time buyers looking to enter the online business world.
- The revenue is unpredictable initially as you build an audience.
- The number of customers is often limited and is often the result of your promotional or marketing activities.
Services-based business model
- The business provides services to clients, often on a per project basis. They can be delivered in person or remotely. In contrast, SaaS business models are accessed remotely.
- Payments are often based on the time and resources required to complete a project.
- The priority is acquiring new customers and hopefully retaining them for long-term projects.
- The revenue is highly unpredictable as it also depends on the number of customers you serve.
- Scalability is impossible, especially if there’s only a single service provider unless projects are outsourced.
Pros and cons of a SaaS business model
While the comparison table above shows the advantages of using a SaaS business model, let’s stay objective in our quest as we tackle the pros and cons below.
What are the pros of the SaaS business model?
- ✅ Scalability – You can scale rapidly as compared to traditional software businesses. This allows for more agility and flexibility in adding new features and users as needed.
- ✅ Predictable cash flow – You typically generate monthly recurring revenue and annual recurring revenue, where customers pay monthly or annually for access to the software. This results in predictable cash flow, making it easier to forecast revenue and plan accordingly.
- ✅ Lower upfront costs – You have a low barrier to entry, allowing even small businesses to access enterprise-level software without the upfront cost of traditional software licenses. This makes it easier for SaaS business owners to compete in their respective industries.
- ✅ Continuous updates – Roll out updates and improvements to your software quickly and efficiently, allowing you to keep up with changing market trends and customer demands. This helps to keep customers engaged and satisfied.
- ✅ Focus on customer success – You have a vested interest in the success of your customers since you rely on ongoing subscriptions for revenue. This often leads to a stronger focus on customer support and success than traditional software companies. And with effective CS software by your side, you can improve your ability to meet these needs efficiently.
What are the cons of using the SaaS business model?
It’s not always a leisurely walk in the park when you run a business with a SaaS model. Remember that there are caveats as well, like the following.
- ❌ Dependence on internet connection – Since you operate through the cloud, you rely heavily on a stable internet connection. This can be a problem for clients operating in remote or underdeveloped regions with limited internet access.
- ❌ Security risks – Storing data in the cloud can create significant security risks for businesses. If your company experiences a data breach, it could lead to the exposure of sensitive data and potential liability issues. This can be especially critical for regulated industries like healthcare or finance.
- ❌ Subscription fatigue – With the explosion of SaaS companies, consumers now have access to vast libraries of software subscriptions. The proliferation of these subscriptions can lead to subscription fatigue, where individuals become overwhelmed with managing all their subscriptions.
- ❌Churn – Since you often rely on recurring revenue, customer churn can be a significant problem. If a customer cancels their subscription, it can lead to a significant loss of revenue, which also requires you to consider Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC). As a result, generating new customers at the same pace can be challenging. That’s why you need to focus heavily on customer retention.
How does a SaaS business generate revenue
Given that customers come and go, I’m sure you want to know how the SaaS business model generates money. Here’s how you can position your brand in terms of pricing strategy.
1. Subscription fees
Subscription fees are a primary revenue stream for SaaS businesses. Users make regular payments to access the software. This model’s predictability and recurring revenue streams have gained popularity.
Netflix utilizes monthly subscription fees. They have diverse pricing tiers, appealing to a wide user base for consistent revenue. Their subscription model enables investment in original content and expansion, leading to dominance in the streaming industry. 
Source: Netflix
2. Usage fees
Essentially, usage fees are charges imposed on customers based on the amount of services they use, such as the number of users, the amount of data or storage, or even the frequency of use.
Klaviyo, a SaaS marketing and automation tool, has a pricing plan based on usage fees. Klaviyo charges its customers based on the number of contacts they have and the number of emails and text messages they send. The pricing is tiered, with different plans available depending on the number of contacts.
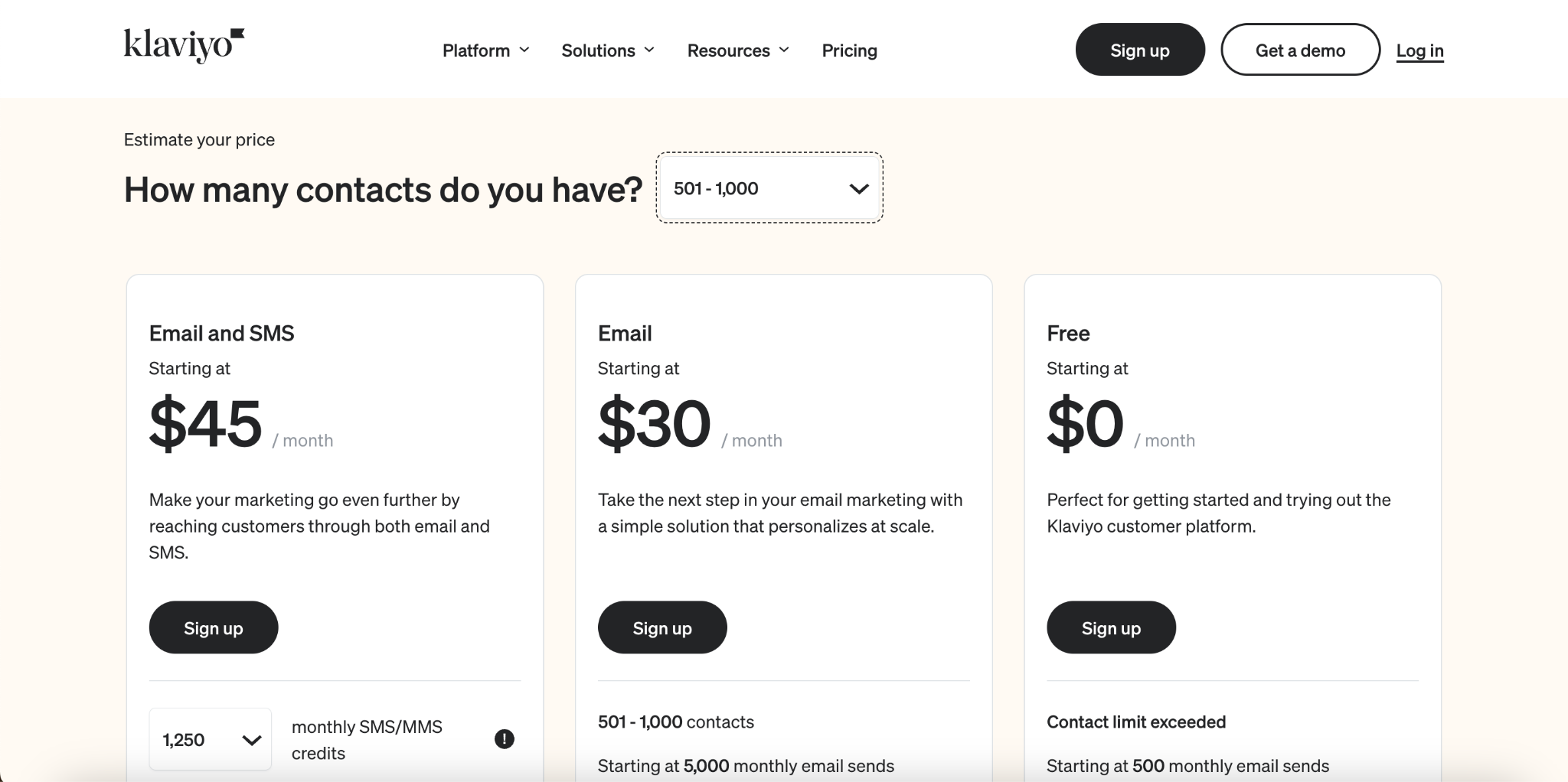
Source: Klaviyo
3. Transaction fees
Transactional fees refer to the fee that users are charged for each transaction they process through the software. Essentially, the business acts as a middleman between the user and the payment processor, taking a small percentage of each transaction as their fee. This fee structure is often paired with transaction monitoring software to ensure the accuracy and security of each payment processed.
Take a look at Stripe, a payment processing company that offers a SaaS platform. Stripe charges a flat 2.9% + 30 cents fee for every transaction processed through their platform. It has allowed them to generate substantial revenue and grow into a billion-dollar company.
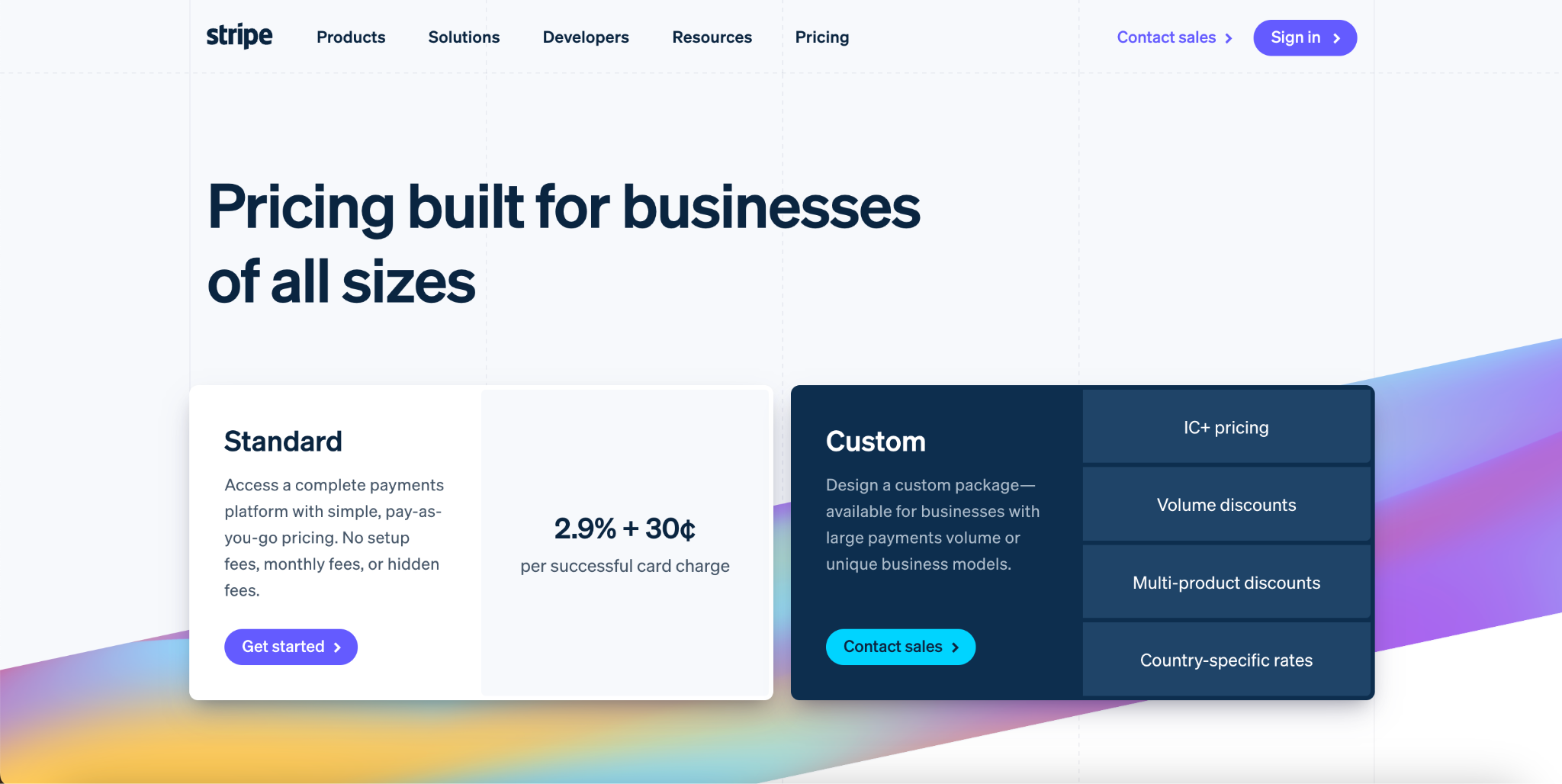
Source: Stripe
3. Upselling
Upselling in SaaS offers extra features or services for an additional fee to customers who have already purchased the base product. The goal is to increase the lifetime value of the customer’s investment and satisfaction with the product while driving more revenue for the business.
An example of upselling in action is Dropbox. Dropbox offers various storage plans to its customers, starting with a free plan with 2GB of storage. Customers can upgrade to Dropbox Plus for additional features like 2TB storage, advanced sharing controls, and remote wipe for lost or stolen devices.
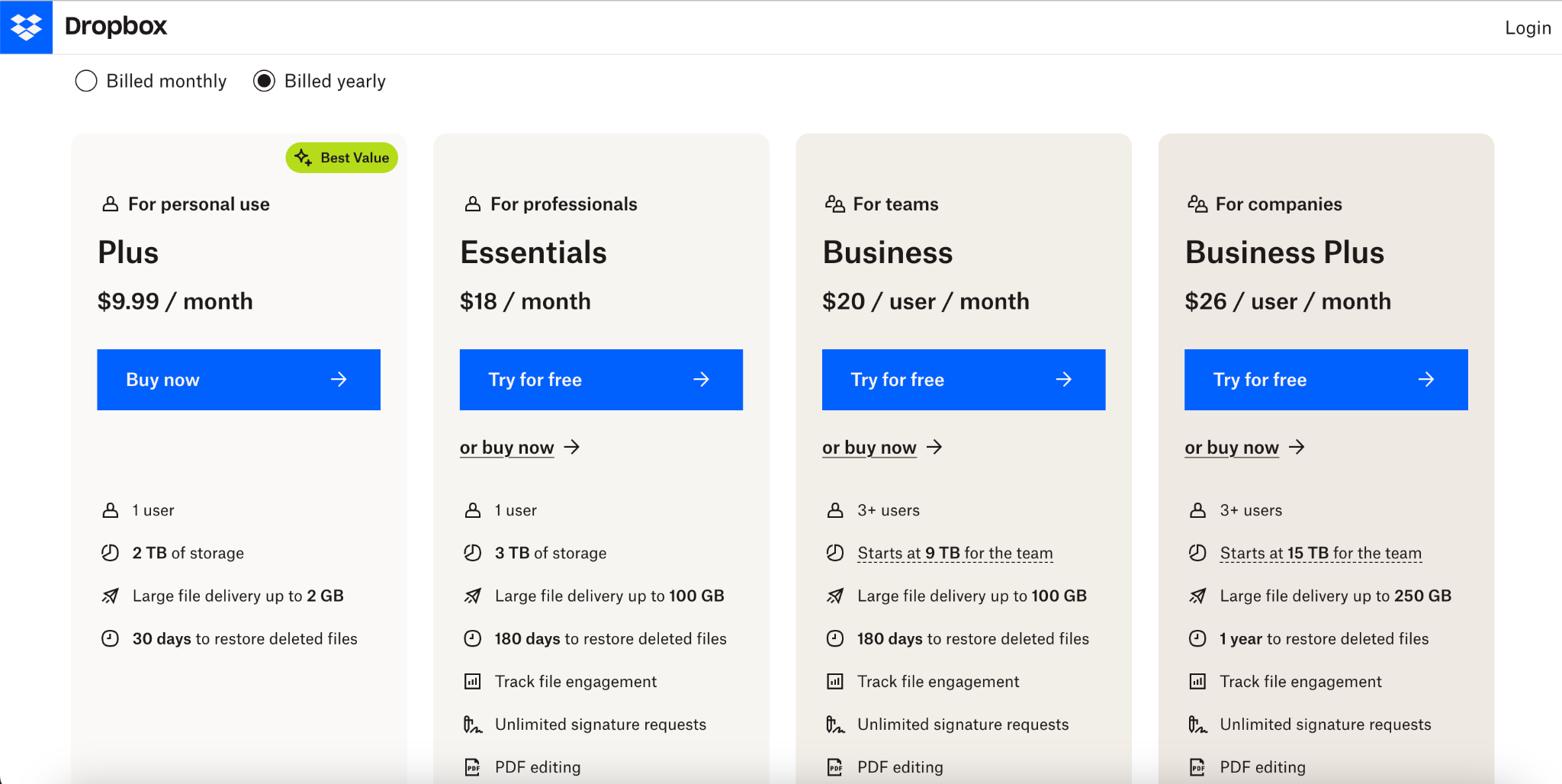
Source: Dropbox
Start your SaaS business with an MVP app
In conclusion, starting your own SaaS business is an excellent choice for budding entrepreneurs and businesses looking to get an edge in their markets.
It’s an opportunity for you to offer cutting-edge solutions that customers seek while providing a platform they can access and share.
Appetiser is the ideal app development partner for building these kinds of applications.
With our proven track record of developing apps that have generated more than $3.5 billion in revenue, we create powerful apps with superior performance that apps users have adored.
So if you want to leap into SaaS ventures today, start your journey with Appetiser and let us take care of all your SaaS development needs.
Your success story is our story, too! Contact us today.

Maria Krisette Lim is a Content Marketing Specialist with 14 years of experience producing web and print ad content. Krisette has a BSBA degree, major in Business Management and Entrepreneurship. When she’s not tinkering with words and punctuation, she’s either curled up with a book while sipping hot tea, playing with her toddler, or tinkering with website builders.